A Frustrated Lewis Pair Mimic Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Imines Using Ammonia Borane
The last decade has witnessed the prosperity of the chemistry of Frustrated Lewis Pairs (FLPs), especially for its ability to active hydrogen. And a great progress on the catalysts development and substrates diversity has been achieved. On the contrary, despite the wide success in the hydrogenation of a variety of unsaturated compounds, few groups have satisfying reports on the asymmetric version of hydrogenation reactions. And among the few successful examples, chiral boron Lewis acids were usually employed for asymmetric induction, which were synthesized and purified by a tedious procedure. In the other hand, the use of readily available chiral Lewis bases for asymmetric hydrogenation has rarely been reported.
The strategy of in situ borane catalyst with chiral alkene (alkyne) hydrocarbons and Piers borane has been developed in Du group. This method is simple and requires no separation and purification of the catalyst; besides, the use of terminal olefins/alkynes, avoid the formation of other diastereisomers. The Lewis acidity of the chiral borane can be adjusted by changing the substituents at the 3,3'-position, whereas the introduction of the chiral alkynes further increases the rigidity of the backbone and enhances the controllability of the chiral borane Lewis acidity. The chiral FLP catalyst has been successfully applied in the high enantioselective hydrogenation of imines, multi-substituted aromatic heterocycles and enol silicon ethers (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6810; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12261; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 623). In addition, the enantioselective hydrosilylation of 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds was achieved for the first time (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 810).

Figure 1. New strategy for in situ preparing chiral borane.
Inspired from the zwitterion species generated from the splitting of H2 by frustrated Lewis pairs, they put forward a frustrated Lewis pair mimic strategy by the combination of Hδ- and Hδ+ incorporated Lewis acid and base together. Piers’ borane and chiral tert-butysulfinamide were chosen as the FLP mimic, and a metal-free asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of imines was realized with high enantioselectivities. Significantly, with ammonia borane as hydrogen source, a catalytic asymmetric reaction using 10 mol % of Piers’ borane, chiral tert-butylsulfinamide, and pyridine additive, has been successfully achieved to furnish optically active amines in 78-99% yields with 84-95% ee’s. This is the first time to realize high enantioselective FLP catalytic conversion using chiral Lewis base, which provides a new idea for the design and development of chiral FLP catalytic system.
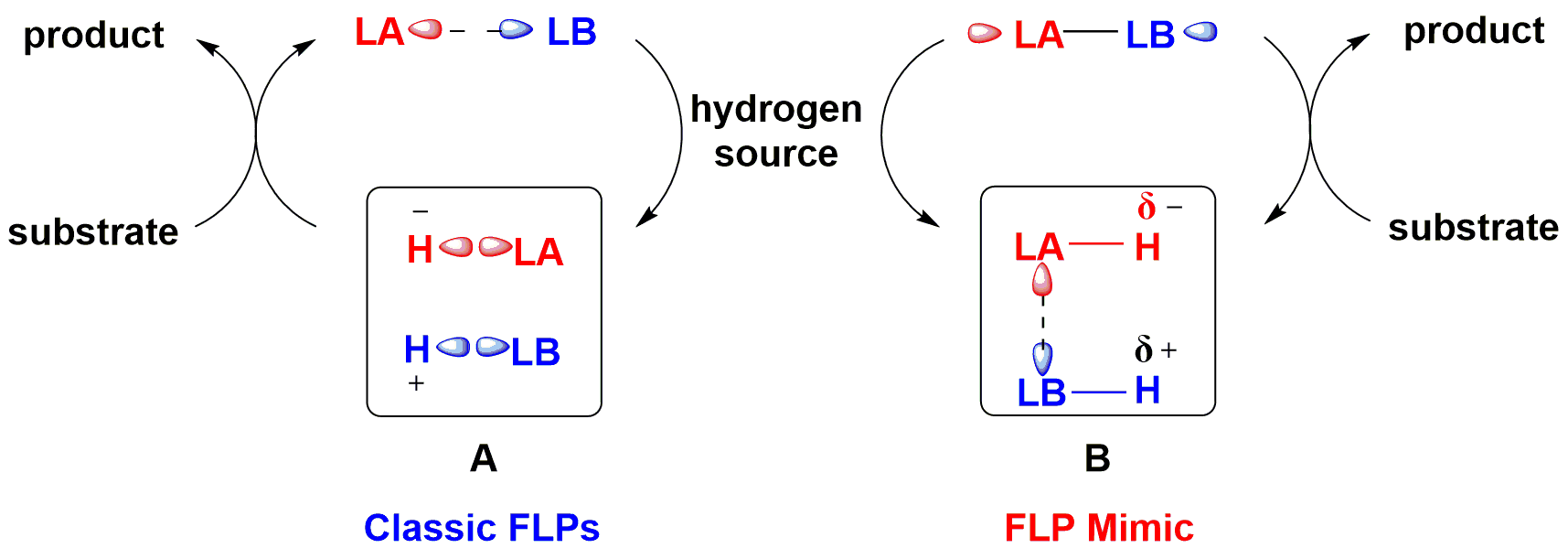
Figure 2. The strategy of mimic FLP.
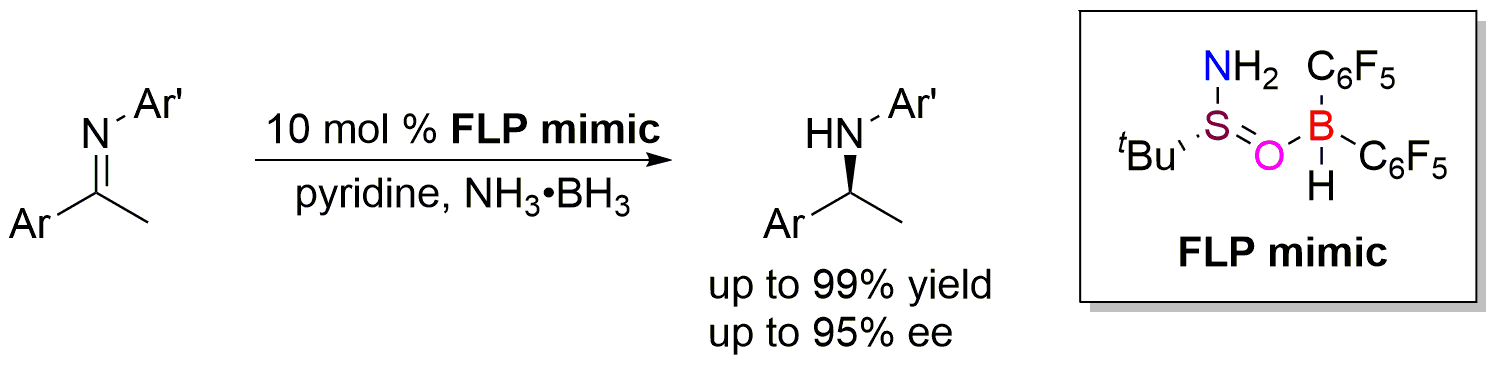
Figure 3. Mimic FLP catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of imines.
Experimental and theoretical mechanistic studies reveal an interesting 8-membered ring hydrogen transfer transition state and an expected regeneration of reactive species with ammonia borane. Accordingly, a plausible catalytic pathway for this reaction is depicted.
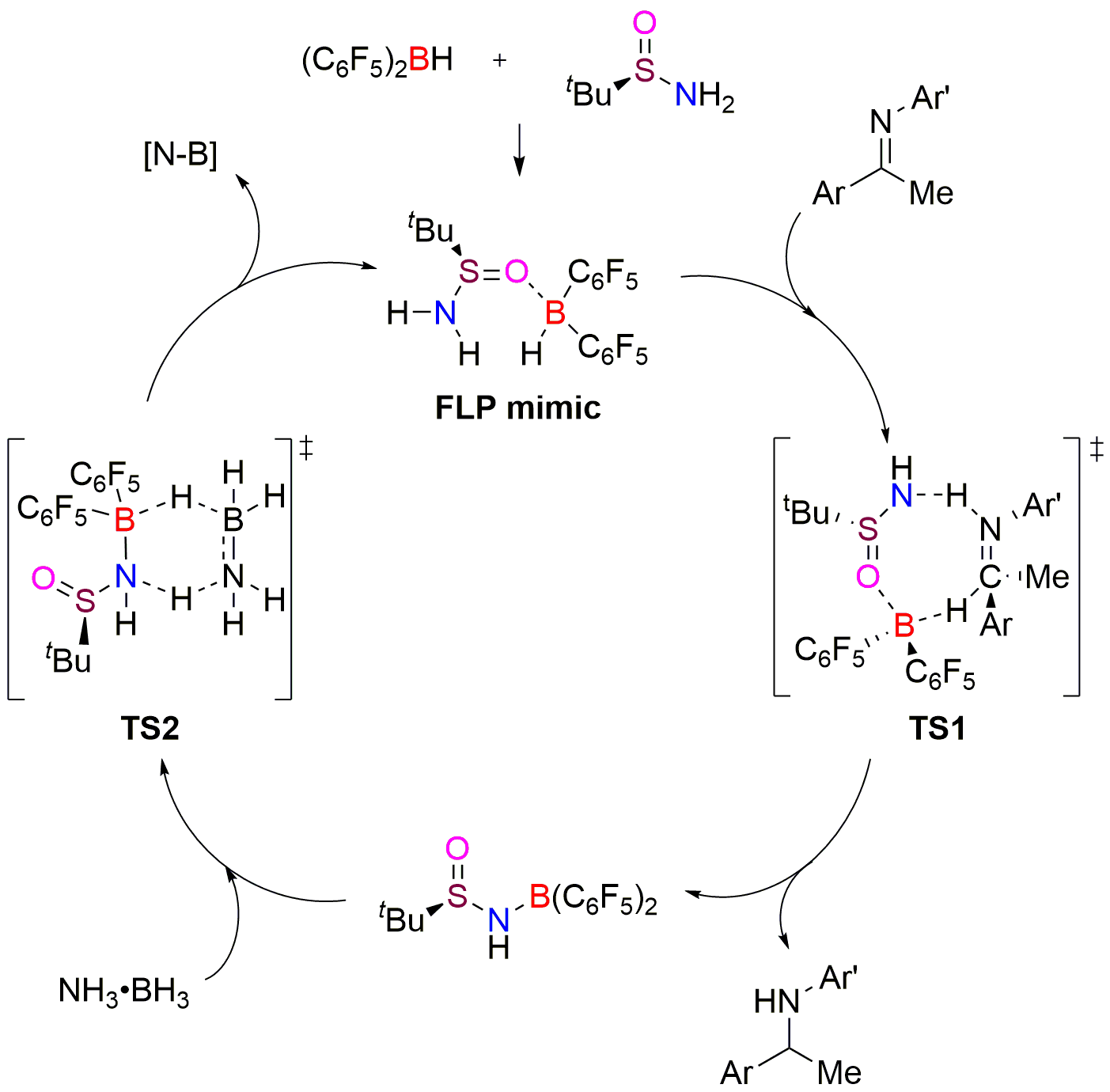
Figure 4. Proposed mechanism of mimic FLP catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation.
(This work has been published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 12956–12962.)

